
Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 State Key Laboratory of Optoelectronic Materials and Technologies, Sun Yat-sen University, Guangzhou 510275, China
2 School of Physics, Sun Yat-sen University, Guangzhou 510275, China
In silicon photonics, the cavity mode is a fundamental mechanism to design integrated passive devices for on-chip optical information processing. Recently, the corner state in a second-order topological photonic crystal (PC) rendered a global method to achieve an intrinsic cavity mode. It is crucial to explore such a topological corner state in silicon photonic integrated circuits (PICs) under in-plane excitation. Here, we study both theoretically and experimentally the topological nanophotonic corner state in a silicon-on-insulator PC cavity at a telecommunications wavelength. In theory, the expectation values of a mirror-flip operation for the Bloch modes of a PC slab are used to characterize the topological phase. Derived from topologically distinct bulk polarizations of two types of dielectric-vein PCs, the corner state is induced in a 90-deg-bend interface, localizing at the corner point of real space and the Brillouin zone boundary of reciprocal space. To implement in-plane excitation in an experiment, we fabricate a cross-coupled PC cavity based on the bend interface and directly image the corner state near 1383 nm using a far-field microscope. Finally, by means of the temporal coupled-mode theory, the intrinsic factor of a cross-coupled cavity (about 8000) is retrieved from the measured transmission spectra. This work gives deterministic guidance and potential applications for cavity-mode-based passive devices in silicon PICs, such as optical filters, routers, and multiplexers.
Photonics Research
2021, 9(8): 08001423
Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 School of Physics & State Key Laboratory of Optoelectronic Materials and Technologies, Sun Yat-sen University, Guangzhou 510275, China
2 e-mail: hext9@mail.sysu.edu.cn
3 e-mail: stszfl@mail.sysu.edu.cn
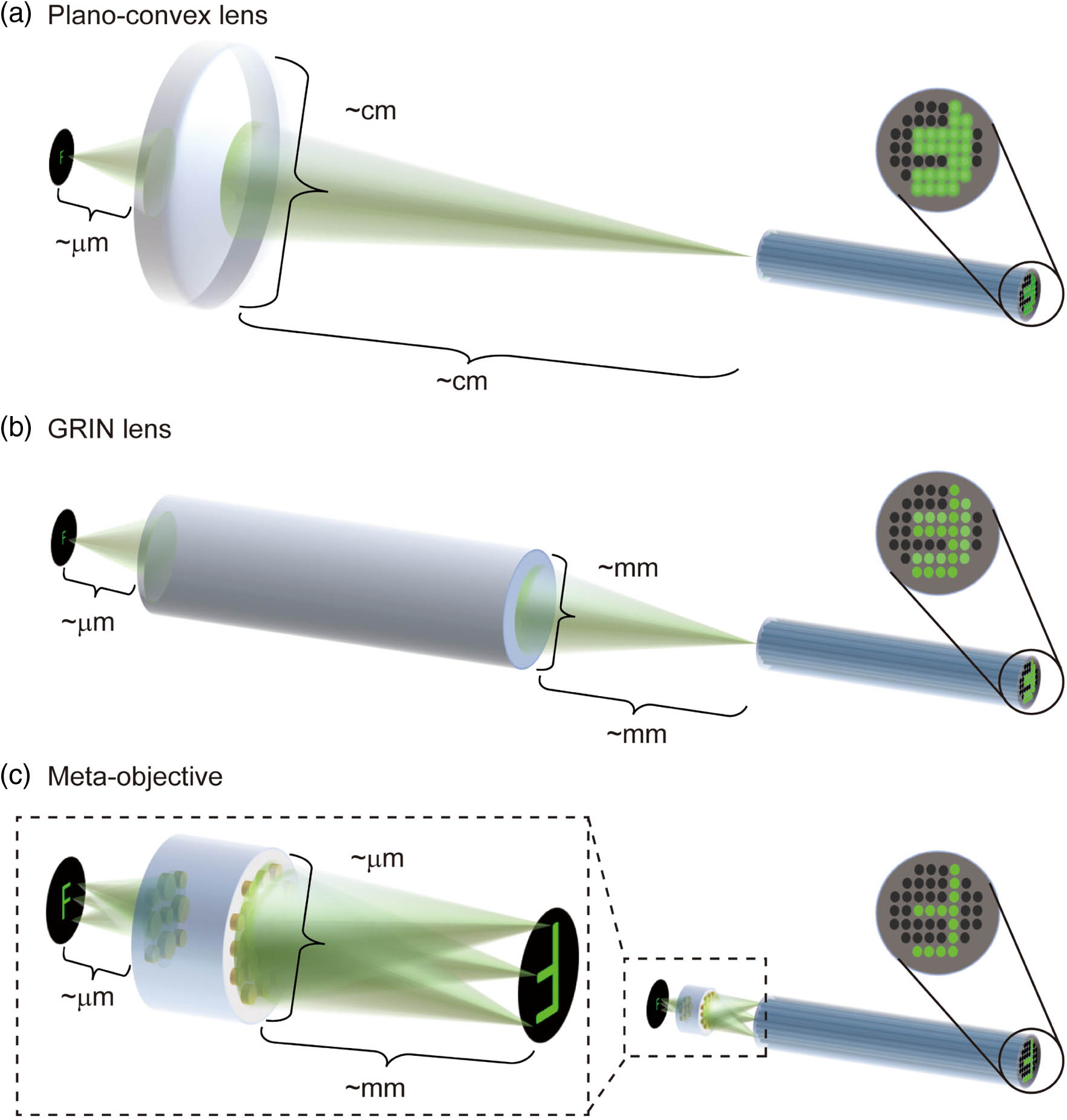
Microendoscopes are vital for disease detection and clinical diagnosis. The essential issue for microendoscopes is to achieve minimally invasive and high-resolution observations of soft tissue structures inside deep body cavities. Obviously, the microscope objective is a must with the capabilities of both high lateral resolution in a wide field of view (FOV) and miniaturization in size. Here, we propose a meta-objective, i.e., microscope objective based on cascaded metalenses. The two metalenses, with the optical diameters of 400 μm and 180 μm, respectively, are mounted on both sides of a 500-μm-thick silica film. Sub-micrometer lateral resolution reaches as high as 775 nm in such a naked meta-objective, with monochromatic aberration correction in a 125 μm full FOV and near diffraction limit imaging. Combined with a fiber bundle microscope system, the single cell contour of biological tissue (e.g., water lily leaf) can be clearly observed, compared to the indistinguishable features in other conventional lens-based fiber bundle systems, such as plano–convex and gradient refractive index (GRIN) cases.
Photonics Research
2021, 9(2): 02000106
中山大学光电材料与技术国家重点实验室, 广东 广州510275
研究了飞秒脉冲经过光子晶体光纤时超连续谱产生的物理机制。 采用输出波长可调谐的钛宝石光参量放大器作为泵浦源, 光纤光谱仪测量不同泵浦功率和不同泵浦波长条件下光子晶体光纤产生的超连续谱的光谱图, 对进行了归一化处理后的不同泵浦功率和不同泵浦波长条件下的超连续谱进行对比, 分析影响光子晶体光纤超连续谱差异的物理机制。 实验结果表明, 当泵浦波长不变时, 随着入射泵浦脉冲平均功率的增大, 波峰增多, 谱宽也逐渐加宽并伴随着出现能量向短波方向集中的现象, 泵浦功率到达一定强度时, 超连续谱的宽度最后到达饱和, 谱的包络趋于稳定; 入射光功率稳定在300 mW时, 超连续谱的宽度和形状皆受到泵浦波长影响, 在760~840 nm范围内, 泵浦波长越长, 波峰数越多, 泵浦脉冲波长离零色散点越近, 光子晶体光纤产生的超连续谱谱宽会越宽, 超连续谱的形状相对越平坦。
光子晶体光纤 超连续谱 飞秒脉冲 Supercontinuum Photonic crystal fiber Femtosecond pulse 光谱学与光谱分析
2015, 35(12): 3283
1 华南理工大学材料科学与工程学院, 广东 广州 510641
2 中山大学理工学院光电材料与技术国家重点实验室, 广东 广州 510275
在飞秒脉冲激光激发下, 观察到了均匀沉积法获得的ZnO纳米颗粒的受激辐射现象, 并从频域和时域两方面研究了ZnO纳米多晶的室温激射特性。 氧化锌纳米颗粒中出现激子-激子散射导致的激射阈值为7.2 GW·cm-2, 激射模式类似于F-P谐振腔模式, 时域谱则表现为寿命曲线中出现快速衰减成分。 与荧光的时间衰减曲线不同, P带时间衰减具有对称结构, 高斯拟合结果只有几个ps, 接近条纹相机的时间分辨率极限。 研究ZnO纳米颗粒的受激发射与激光特性对揭示ZnO晶体的内部结构和激子激发态的性质、 激光产生的机理等有重要意义。
ZnO纳米颗粒 时间分辨 受激发射 ZnO nanoparticles Time resolved Stimulated emission 光谱学与光谱分析
2009, 29(6): 1459
1 中山大学理工学院, 光电材料与技术国家重点实验室, 广东 广州 510275
2 华南理工大学材料科学与工程学院, 广东 广州 510641
室温下获得了均匀沉积法制备的纳米ZnO颗粒在低能量2.33 eV 光子(532 nm)的准连续皮秒脉冲激发下的频谱范围从550~1 000 nm的时间分辨光谱和时间积分光谱。 随着样品粒径的增加, 发光带谱带峰值出现规律性的红移。 通过高斯拟合对光谱结构解迭发现, 这种规律性的红移是由于低能端区域的高斯组分的相对比例增加所致。 时间分辨光谱中超快发射的荧光衰减寿命(皮秒量级)也出现随着样品粒径的增大而相应变长。 源于材料尺寸、 纳米颗粒大的比表面积所引起的表面能级可以较好的解释此范围的超快发射特性。
纳米ZnO颗粒 时间分辨光谱 表面态 ZnO nanoparticles Time-resolved photoluminescence Surface states 光谱学与光谱分析
2009, 29(5): 1160
应用Matlab语言,结合博奇型计算全息的编码方法,利用计算机分别绘制了菲涅耳全息图和傅里叶变换全息图,实现了计算全息图的快速制作,讨论了制作计算全息图的原理、方法和步骤。利用CGH技术和数字全息技术所生成的全息图再现出原始图像,完成了全息图的数字重现,实现了整个全息记录和再现过程的计算机模拟。与传统的编程语言和绘图方法相比较,该算法在实现上更加简单和快捷,并且带有一系列提高计算全息图质量的措施,有效地消除了零级像和孪生像的影响,获得了清晰的数字再现图像。
计算全息图 傅里叶变换 菲涅耳全息图 数字再现 computer-generated hologram Fourier transform Fresnel hologram Matlab Matlab digital reconstruction
1 中山大学光电材料与技术国家重点实验室,广州 510275
2 中山大学高分子研究所, 广州 510275
采用超快激光光谱技术研究了一种新型的卟啉侧链聚合物(HTPP-PGMA)的激发态动力学过程.研究结果表明:HTPP-PGMA的荧光弛豫过程远快于通常的小分子卟啉单体化合物的荧光弛豫过程.在近共振波长(λ=532 nm)处,观察到了HTPP-PGMA的瞬态无腔光学双稳态的响应过程.通过采用电荷转移模型对HTPP-PGMA的超快激发态动力学过程进行了分析.





